How Plate Heat Exchangers Work [Breakdown]
Posted by JEFFREY LUFF
Why Understanding Plate Heat Exchangers Matters
Whether you're working in HVAC, renewable energy, industrial manufacturing, or just trying to improve the performance of your outdoor wood boiler, choosing the right plate heat exchanger can mean the difference between long-term performance and constant frustration.
In this guide, we’ll cover:
- What plate heat exchangers are
- How they work
- Different types available
- Their top use cases
- Why they outperform other designs
What Are Heat Exchangers?
At their core, heat exchangers move heat between two fluids (liquid or gas) without letting those fluids mix.
They do this by separating the fluids with a solid barrier (usually metal) that conducts heat. That way, energy is transferred, but the fluids stay isolated.

Plate Heat Exchangers (PHEs)
Instead of using a large shell or coil, PHEs rely on a series of thin metal plates stacked together. Each plate creates a pathway for fluid to flow, and the alternating arrangement allows one hot fluid and one cold fluid to run side by side, constantly exchanging energy across the surface.

Why do we use them? Because they:
- Offer a huge amount of surface area in a small space
- Can be easily customized for different flow rates or temperatures
- Are highly efficient and cost-effective
Different Plate Heat Exchanger Options
While all plate heat exchangers share the same core principle, they come in several configurations designed for different use cases.
Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers
- Sealed units made by brazing thin metal plates together
- No gaskets, which means fewer leaks and compact design
- High pressure & high temperature tolerance
Common uses:
- HVAC systems
- Oil and refrigerant cooling
- Hydronic heating
- Renewable energy systems
Pros: Compact, efficient, durable
Cons: Cannot be taken apart for cleaning, must be replaced if clogged or damaged
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers
- Uses gaskets between each plate, allowing for disassembly
- Easy to clean, inspect, or add/remove plates as needed
- Ideal for systems prone to scaling, sediment, or maintenance
Common industries:
- Food and beverage
- Pharmaceuticals
- Chemical processing
Pros: Maintainable, flexible
Cons: Gaskets may wear over time and need replacing
Dragon Plate Exchangers (Specialized Models)
Designed specifically for the outdoor wood boiler industry.
According to Jeff from Alternative Heating:
“Our Dragon Plate Exchangers use thicker metal and wider spacing to resist sediment wear, giving you a longer-lasting unit even with the gunk that comes from untreated or open-loop boiler water.”
- Built to handle sediment-rich systems
- Thick plate walls = more durability
- Slightly reduced efficiency, but increased longevity in dirty water conditions
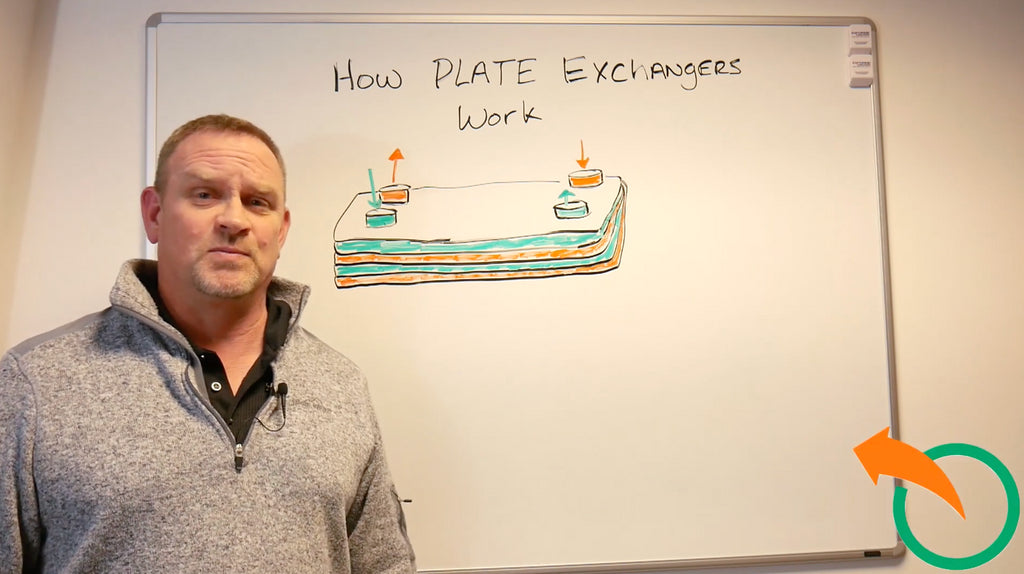
Step-by-Step on How a Plate Heat Exchanger Works
Let’s simplify it with a real-world analogy.
“Imagine shaking hands, your warm hand touches someone else’s cold hand. Your warmth transfers to theirs, but your blood never mixes. That’s what happens inside a plate exchanger.”
Here’s how it plays out step-by-step:
- Fluid Entry: Two fluids enter the unit through opposing ports.
- Hot fluid in one set of channels
- Cold fluid in the alternating channels
- Heat Transfer Surface: The thin plates separate the fluids, but allow heat to pass between them.
- Each plate increases surface area
- Corrugations or "waffle patterns" create turbulence for better transfer
- Flow Arrangement: Typically counterflow (fluids moving in opposite directions), which maximizes heat exchange.
- Thermal Exchange:
- The hot fluid loses heat through the plate
- The cold fluid absorbs that heat and exits warmer
- Exit: Both fluids leave at new, adjusted temperatures.
Efficiency Factors:
- Material (stainless steel, titanium)
- Number of plates
- Plate spacing & thickness
- Pattern design (turbulence-enhancing corrugations)
Applications of Plate Heat Exchangers
Here’s where you’ll find plate heat exchangers hard at work:
Heat exchange systems support a wide range of industries, each with its own set of critical applications. In HVAC, these systems are used for chillers, boilers, and geothermal setups that help maintain efficient temperature control in residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. The refrigeration sector relies on similar technology to power condensers and evaporators, ensuring reliable cooling performance for storage and processing environments.
Food and beverage operations also depend heavily on precise thermal management. Heat exchange equipment supports pasteurization, dairy cooling, and brewing, all of which require tight temperature regulation to maintain product quality and safety.
Across industrial settings, these systems are essential for oil cooling, chemical processing, and water heating, helping facilities operate safely and efficiently. Renewable energy applications make use of heat exchangers as well, particularly in solar thermal projects and heat pump systems that convert natural energy sources into usable power.
In automotive and marine environments, heat exchange equipment plays a vital role in engine cooling and fuel preheating, supporting performance, efficiency, and long-term reliability across demanding operating conditions.
Their small footprint, high efficiency, and flexibility make them ideal wherever reliable heat transfer is needed.
Advantages of Plate Heat Exchangers
Let’s compare plate exchangers to more traditional designs like shell-and-tube units.
Plate heat exchangers offer high thermal efficiency in a compact footprint, making them ideal for systems where space and performance matter. Their maintenance is straightforward, especially with gasketed designs, and they allow easy expandability by adding or removing plates as system demands change. When built with the right materials, they deliver strong durability and typically result in lower long-term costs.
Shell-and-tube heat exchangers provide moderate thermal efficiency and require more space due to their larger design. Maintenance needs are generally higher, and their ability to scale is limited. While they are durable, they come with higher upfront and operating costs compared to plate models.
Other Benefits:
- Better energy recovery in industrial systems
- Lower emissions due to improved efficiency
- Reduced water and energy usage
Why Plate Heat Exchangers Are a Smart Choice
Plate heat exchangers are among the most efficient, compact, and cost-effective heat transfer tools available.
Whether you’re installing one in a wood boiler system, an HVAC loop, or a brewery, understanding how they work helps you:
- Choose the right type for your needs
- Avoid clogging and corrosion
- Extend the lifespan of your system
We’ve built our Dragon Plate Exchangers specifically to address the challenges of wood boiler systems (like sediment and open-loop exposure) so they last longer in real-world conditions.
Ready to Shop or Learn More?
Whether you’re upgrading your current system or building something new, we carry numerous plate heat exchangers designed to handle real-world conditions—especially in wood boiler setups.
Still not sure which one is right for you? Check out our YouTube walkthrough for a visual breakdown, or give us a call. We’re always here to help.
Stay efficient. Stay heated.
